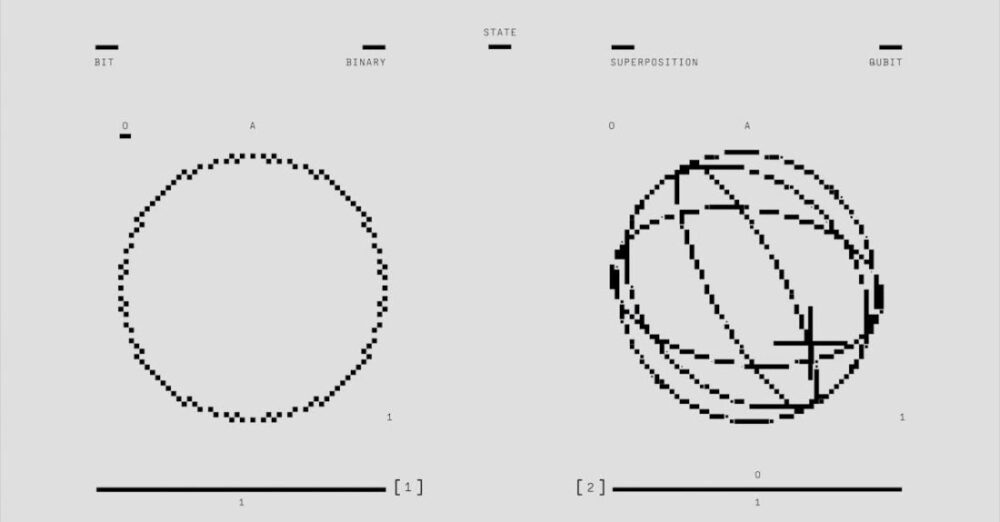
Quantum computing is a revolutionary technology that has the potential to transform the way we process information and solve complex problems. While traditional computers rely on bits to store and process data, quantum computers use qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously thanks to the principles of quantum mechanics. This capability allows quantum computers to perform calculations at an unprecedented speed, making them a game-changer in various fields, including data security.
**The Threat to Current Encryption Methods**
One of the most significant impacts of quantum computing on data security is its potential to render current encryption methods obsolete. Most of the encryption algorithms used today, such as RSA and ECC, rely on the difficulty of factoring large numbers for their security. However, quantum computers have the ability to solve these complex mathematical problems much faster than classical computers, posing a serious threat to the security of encrypted data.
**Breaking Encryption**
Quantum computers have the potential to break encryption by quickly factoring large numbers that are the basis of many encryption algorithms. For example, RSA encryption, which is widely used to secure data transmitted over the internet, could be vulnerable to attacks from quantum computers. This means that sensitive information such as financial transactions, personal communications, and government data could be at risk of exposure if quantum computing advancements outpace the development of quantum-resistant encryption methods.
**Post-Quantum Cryptography**
To address the threat posed by quantum computing to data security, researchers are actively developing post-quantum cryptography algorithms that can resist attacks from quantum computers. These new encryption methods are designed to be secure against quantum attacks while remaining efficient for use in practical applications. By transitioning to post-quantum cryptography, organizations can ensure the long-term security of their data in the age of quantum computing.
**Quantum Key Distribution**
In addition to post-quantum cryptography, another approach to enhancing data security in the quantum computing era is the use of quantum key distribution (QKD) protocols. QKD leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to enable secure communication channels between parties by using quantum states to generate encryption keys. Unlike traditional encryption methods, which rely on mathematical complexity, QKD offers a theoretically unbreakable method of key distribution that is immune to quantum attacks.
**Enhanced Data Protection**
The development of quantum computing also presents opportunities to enhance data security through quantum-resistant encryption techniques. By leveraging the unique properties of quantum mechanics, researchers are exploring new encryption algorithms that can withstand attacks from quantum computers. These quantum-resistant algorithms offer a promising solution to the challenges posed by quantum computing and provide a pathway to securing sensitive information in the quantum era.
**The Future of Data Security**
As quantum computing continues to advance, the impact on data security will become more pronounced. Organizations must stay ahead of the curve by implementing quantum-resistant encryption methods and exploring innovative technologies like quantum key distribution to protect their data from emerging threats. By embracing the opportunities presented by quantum computing while mitigating its risks, we can ensure a secure and resilient foundation for the digital future.
In conclusion, the rise of quantum computing has profound implications for data security, challenging the effectiveness of traditional encryption methods and necessitating the development of quantum-resistant solutions. By investing in post-quantum cryptography, quantum key distribution, and quantum-resistant encryption algorithms, we can safeguard our data in the face of evolving threats posed by quantum computing. As we navigate the transition to a quantum-empowered world, proactive measures to enhance data security will be essential to preserving the confidentiality and integrity of information in the digital age.





